Healthcare providers have been offering remote services for years, which have allowed patients to receive healthcare from the comfort of their own homes.
However, following the COVID-19 pandemic, telemedicine services became a necessity and are now a common tool utilized by many patients and healthcare professionals.
Why? These phone and video calls help patients protect themselves and others as well as provide a host of other benefits (but more on this later!)
In this article, we’ll discuss what telemedicine is, the types of telemedicine, and when patients should be using these services. Let’s dive in.
What is Telemedicine?
Telemedicine allows healthcare providers to connect with patients without an in-person visit. Telemedicine services are provided primarily online or via smartphone through video chats or phone calls.
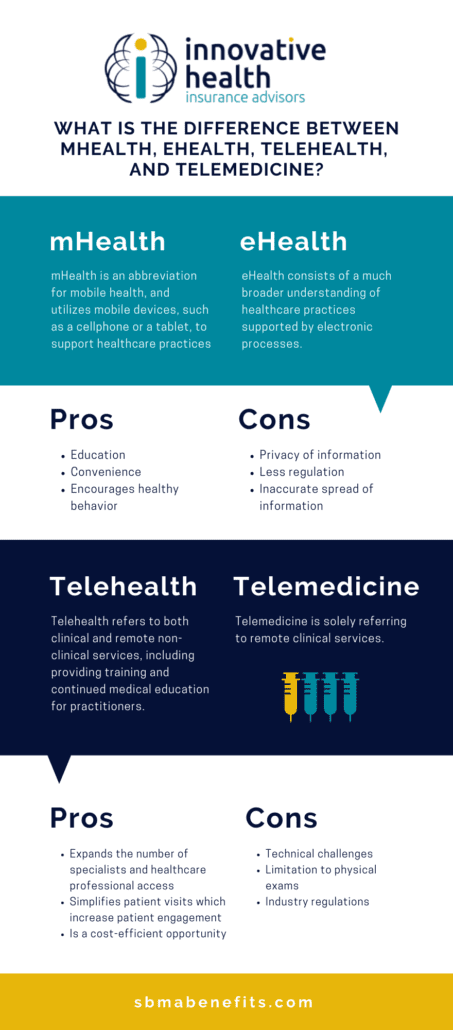
What is the Difference Between Telehealth and Telemedicine?
The terms “telemedicine” and “telehealth” are often used interchangeably, though the two have a few key differences: telemedicine refers specifically to remote clinical services and telehealth can refer to remote non-clinical services.
Telemedicine, as stated by the World Health Organization, is “healing from a distance.” You receive treatment without an appointment or visiting the office.
Telehealth uses electronic information to support long-distance clinical healthcare, education, and administrative activities. It improves patient care and physician education rather than providing a service. Telehealth involves scheduling appointments, medical education continuation, and training for physicians.
In short, all telemedicine is telehealth, but not all telehealth is telemedicine.
Types of Telemedicine
Using telemedicine, you can discuss symptoms and medical issues, receive a diagnosis, learn treatment options, and get prescriptions. There are a few common types of telemedicine which include:
Real-Time or Interactive Medicine
Interactive telemedicine, also commonly referred to as real-time or live telemedicine, involves a physician and patient communicating in real-time.
Real-time telemedicine involves any two-way communications –such as video conferencing and phone calls – that let providers and patients talk and allows healthcare providers to offer medical care.
Some common services provided via interactive telemedicine include assessments of medical history, basic visual examinations, psychiatric evaluations, and even ophthalmic tests.
Remote Patient Monitoring
Remote patient monitoring gives caregivers the ability to monitor patients who have medical equipment that collects information like blood pressure, blood sugar levels, and more.
Through technology, information is sent to healthcare professionals and allows them to provide care and keep an eye on patients without the patients needing to visit in person.
Remote patient monitoring can result in benefits such as reducing the time a patient needs to be in the hospital, reducing a patient’s exposure to other illnesses present in a healthcare building, as well as giving the patient time to recover at home.
Remote patient monitoring is especially effective for chronic conditions such as heart disease, asthma, and diabetes.
Store and Forward Practices
In telemedicine, store and forward practices allow providers to share their patient’s information with other healthcare specialists and professionals.
The most significant advantage of these practices is that it doesn’t require the simultaneous attention of the delivering and receiving parties.
Many healthcare professionals—such as field technicians, caregivers, or specialists, for example—can collect the necessary data and upload it for use by other healthcare professionals.
When Should You Use Telemedicine?
Telemedicine is for straightforward questions and issues, and any follow-up consults. It also can be helpful with psychotherapy and teledermatology. Some examples of straightforward issues include cold and flu symptoms, insect bites, diarrhea, pink eye, and sore throats.
Telemedicine has advanced our current health care options by offering several new benefits. It is making healthcare accessible for more patients, whether they live in a remote location, have a packed schedule, or any number of other reasons.
When Should You NOT Use Telemedicine?
Telemedicine is not for emergencies. For anything that requires urgent, primary care, you should go to a doctor in person.
Benefits of Telemedicine
Telemedicine Saves Time
These services also help people avoid unnecessary hospital visits, which helps healthcare professionals give advice at a distance, save time, and reduce costs for both patients and doctors. Not only will it help avoid hospital visits when they aren’t necessary, but it will also give patients in the hospital the ability to discharge sooner by monitoring their vitals with telemedicine.
Telemedicine is Affordable
A recent study found that the average telemedicine visit is around $79, whereas an average doctor’s appointment is $149, and a trip to the emergency room costs, on average, $1,734. As telemedicine continues to grow, health insurance providers are offering coverage for telemedicine visits. Some states even require that health insurance plans reimburse patients for telemedicine visits.
Telemedicine is Accessible
Telemedicine offers a more accessible opportunity for healthcare and changes the way we visit the doctor. At Innovative HIA, we offer the most competitive limited benefit plans in the industry, including virtual health options! Check out our services for more information!
Read on for the pros and cons of telemedicine.