Article originally published on SBMA Benefits.
The digital health world has seen massive growth over the last year. eHealth, mHealth, telehealth, and telemedicine are used to describe the use of mobile and desktop technology for patient management. These terms are used interchangeably at times, however, they each represent a different aspect of technology and healthcare.
Learn about the difference between eHealth, mHealth telehealth, and telemedicine below, and why it’s important to know the difference.
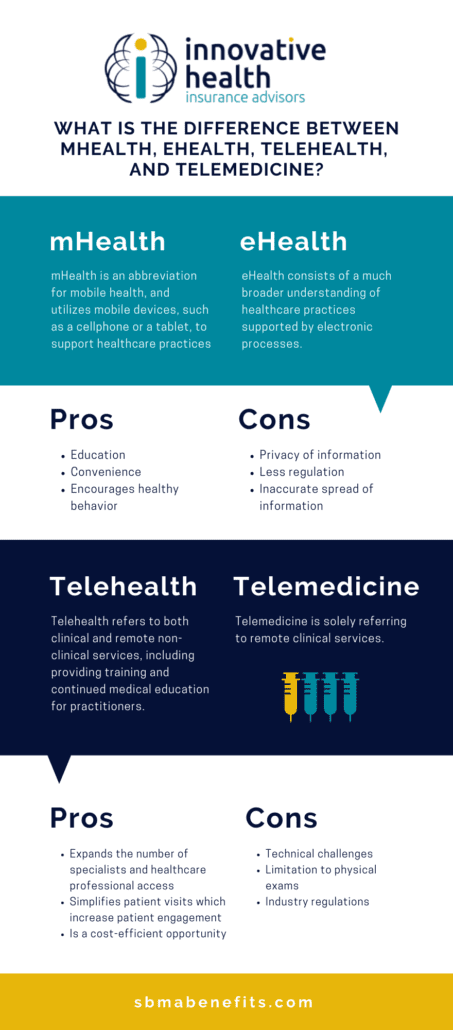
The Difference Between mHealth and eHealth
Both mHealth and eHealth play a role in supporting healthcare with electronics. They perform similar functions, however, the means by which the information is provided is the primary difference.
What is mHealth?
mHealth is an abbreviation for mobile health, and utilizes mobile devices, such as a cellphone or a tablet, to support healthcare practices. With mHealth services, patients are able to log, store, and monitor their health records on their personal mobile devices. These applications are helpful in improving the efficiency of the delivery of healthcare information. mHealth applications can be helpful in research, and practitioner and patient use.
Health tracking apps on mobile devices are becoming increasingly popular during everyday use. There are over 318,000 health apps on the market to choose from. Popular health app examples of mHealth include:
- Fitbit
- GoogleFit
- Apple Heart Study
mHealth has the ability for healthcare professionals to track the recovery of patients.
As hospitals and healthcare become more technologically reliant, more and more hospitals and health facilities are using the resources apps provide to access records, make appointments, and ask questions from mobile devices.
What is eHealth?
On the other hand, eHealth consists of a much broader understanding of healthcare practices supported by electronic processes. The technology used to improve healthcare practices with eHealth include electronic health records, patient administration systems, lab systems, and other records that cannot be stored within mobile health applications.
According to the Journal of Medical Internal Research, there are 10 “e’s” in eHealth
- Efficiency- avoid unnecessary duplication and streamline the health care service between patient and provider.
- Enhancing quality- providers have access to each other’s notes to avoid duplicating any previous exams or studies.
- Evidence based- there should still be scientific evidence on the basis of all information provided in eHealth.
- Empowerment- it should empower patients to be a part of the medical process.
- Encouragement- improving the relationship between healthcare provider and patient to work together in a partnership.
- Education- healthcare providers and patients have increased educational resources to learn and implement.
- Enabling- allowing easy communication between healthcare providers and patients across the board.
- Extending- allowing healthcare services and assistance across the globe instead of relying on your set geographical location.
- Ethics- maintain the same values of professional practice, informed consent, privacy and equity.
- Equity- make healthcare more equitable for users.
Furthermore, it should be easy-to-use, entertaining, and exciting.
Pros and Cons of mHealth and eHealth
Like everything else, there are pros and cons to using the digital capabilities of mHealth and eHealth.
Pros of mHealth and eHealth
- Education
- Convenience
- Encourages healthy behavior
These three elements make mHealth and eHealth valuable tools for users. It’s a form of education for users to understand medical terminology easily, learn more about anatomy, prescription medication, and provide the ability to research using medical literature.
We live in a world of convenience. Having technology on easily accessible smartphones keeps information at the tip of a finger, wherever users are. It can provide reminders about appointments or medications and much more by streamlining the communication processes. Health care providers have easier digital access to records and information instead of relying on paper documents.
Finally, these digital services act as a platform to encourage healthy behavior through reminders or even encouragement from doctors.
Cons of mHealth and eHealth
- Privacy of information
- Less regulation
- Inaccurate spread of information
Like all digital information, the material presented in apps is susceptible to data breaches and hackers. There is also the potential that an app could share personal and private user information.
Additionally, these apps contain information that is less regulated than the information published in medical journals. Using them to test for the blood pressure may also lead to inaccurate results.
Consider the pros and cons when using mHealth to support healthcare practices.
The Difference Between Telehealth and Telemedicine
These terms are confused with one another and used interchangeably. However, like eHealth and mHealth one term serves a broader purpose. The broader term in this comparison is telehealth. Telehealth refers to both clinical and remote non-clinical services, including providing training and continued medical education for practitioners.
Telemedicine is solely referring to remote clinical services. The concept of telemedicine was started to treat patients who are located in remote areas. Throughout the last year with more and more services relying more on virtual resources, it has served a greater purpose – providing people access to care without putting themselves at risk of contracting COVID-19. As more people gain access to these services, expectations around waiting room times, access to care, and convenience of care are changing.
Understanding the ways the terms work together to create the big picture of virtual healthcare is crucial to understanding your access to care. The aim of all of these services is to provide greater quality, efficiency, and cost of care to both practitioners and patients. Each plays a unique role in crafting a well-rounded digital healthcare plan for patients.
Pros and Cons of Telehealth and Telemedicine
Like mHealth and eHealth, the usage of telehealth and telemedicine can have positive and negative effects. Let’s uncover what they are.
Pros of Telehealth and Telemedicine
- Expands the number of specialists and healthcare professional access
- Simplifies patient visits which increase patient engagement
- Is a cost-efficient opportunity
Technological expansions now allow patients access to a wider net of specialists and healthcare professionals. Traveling to a provider is less of a concern with video capabilities. This helps patients who live in a different location see a wider range of healthcare professionals, or help patients see a provider for visits that do not require an in-person exam.
Patient engagement is crucial for the success of their treatment plan. Telehealth and telemedicine services give patients quick access to providers and supporting staff in case treatment plans need alteration. It also helps practitioners to check in with patients conveniently and encourages the continuation of care plans.
Overall, telehealth and telemedicine services are more cost-effective for patients and health care professionals. It saves time traveling and time in the waiting room. Additionally, virtual payment methods are quick, easy and reduce paper billing processes.
Cons of Telehealth and Telemedicine
- Technical challenges
- Limitation to physical exams
- Industry regulations
On the flip side, technology itself poses challenges. Hardware, software, and wireless connection aren’t foolproof. They can malfunction without notice or in the middle of a virtual exam. Some users may even find switching to technology a more difficult barrier to overcome.
While video conferencing an appointment with a healthcare provider works for certain visits, they may not in all instances. There are times when seeing a provider in person will help find the answers needed for a treatment plan.
Each state has different rules and regulations when it comes to telehealth and telemedicine practices. It may become muddled to decipher waivers and procedures needed during a growing virtual era. As we rely heavily on technology, there are rising concerns regarding how safe and protected information is from hackers and data breaches.
Overall, telemedicine and telehealth have pros and cons, similar to mHealth and eHealth pros and cons. Weighing the benefits and the drawbacks of both help make better, well-informed decisions.
At Innovative HIA, we believe in providing our clients with the most affordable, efficient benefits that are tailored to the needs of their employees. Telemedicine services integrate seamlessly into your benefits package to ensure your employees remain healthy and happy.
To learn more about telehealth and why it’s here to stay, read our article here.